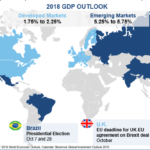
The year 2026 marks a critical inflection point for corporate ethics and responsibility. Businesses face unprecedented convergence of technological disruption, geopolitical fragmentation, and environmental degradation. Traditional frameworks for ethical decision-making struggle to keep pace with these accelerating changes.
Artificial intelligence penetrates every business function, promising efficiency gains while threatening workforce stability. Geopolitical tensions fracture global markets, challenging the foundations of international commerce. Environmental crises multiply beyond our capacity to control them individually.
Yet amid this turbulence, business ethics remains essential—not as compliance theatre but as strategic compass. Companies that anchor decisions in clear values will navigate uncertainty more successfully than those chasing short-term gains. The question is no longer whether ethics matters, but how to operationalize it effectively.
This year tests which organizational changes will endure and which represent temporary overreactions to pressure. Leaders must distinguish between necessary transformation and destructive cost-cutting masquerading as innovation. The decisions made now will shape corporate cultures for decades.
Stakeholders increasingly demand authenticity, not aspirational statements divorced from operational reality. Investors scrutinize environmental, social, and governance performance with unprecedented rigor. Consumers reward brands whose values align with their own.
Employees seek purpose beyond paychecks, particularly as AI threatens job security across sectors. Communities expect corporations to contribute positively to local ecosystems, not merely extract value. Regulators worldwide tighten requirements around due diligence, transparency, and accountability.
Business ethics in 2026 requires courage to resist expedient choices that compromise long-term viability. It demands wisdom to balance competing stakeholder interests amid genuine scarcity and trade-offs. It necessitates humility to acknowledge limits of human knowledge and control.
This article explores three defining trends shaping business ethics today: AI’s human cost, geopolitical chaos, and environmental imperatives. Each presents distinct challenges requiring ethical clarity to navigate successfully.
AI Transformation and the Human Cost of Efficiency
Artificial intelligence now permeates strategic planning, operational execution, customer service, and product development. Companies deploy AI to optimize supply chains, automate customer interactions, enhance marketing precision, and accelerate innovation cycles. The technology promises unprecedented efficiency gains and competitive advantages.
Negative Business Implications of Myopic AI Implementation
But 2026 exposes the darker implications of aggressive AI adoption without ethical guardrails. Mass downsizing accompanies automation across industries, from manufacturing floors to corporate headquarters. Finance, human resources, customer service, and even creative functions face significant workforce reductions. Many organizations approach AI implementation purely through cost-cutting lens, measuring success by headcount reduction. This myopic perspective ignores profound risks to institutional knowledge, customer relationships, innovation capacity, and brand reputation. Short-term savings often mask long-term value destruction.
- Customer experience suffers when companies replace human judgment with algorithmic responses lacking contextual awareness. Automated systems struggle with nuanced situations requiring empathy, creativity, or ethical reasoning. Frustration mounts as consumers encounter chatbots unable to address genuine concerns.
- Quality deteriorates when organizations eliminate experienced professionals who understood product intricacies and operational complexities. AI systems trained on historical data cannot anticipate novel challenges or exercise judgment beyond programmed parameters. Errors compound when no humans remain to catch them.
- Innovation stagnates despite AI’s creative potential because breakthrough thinking requires diverse human perspectives. Homogeneous algorithms optimize existing approaches but rarely generate paradigm-shifting insights. Companies downsizing creative talent undermine their own competitive futures.
- Asset valuation increasingly disconnects from fundamentals when balance sheets strip out human capital investments. Financial models celebrating “efficiency” through workforce reduction ignore that sustainable competitive advantage derives from people. Organizations hollowed out by cost-cutting become acquisition targets, not industry leaders.
Leveraging Ethics to Gauge AI Value Add Beyond Short Term Business Benefits
The ethical imperative is understanding what AI adds and does not destroy beyond short term benefits. Automation suited for repetitive, rules-based tasks becomes destructive when applied to complex human judgment situations. Leaders must resist pressure to eliminate positions simply because technology enables it. Adopt a broader perspective on quality, knowledge, values, and customer empathy, which enable the company to build on sustainable value creation. Responsible AI implementation requires assessing impacts beyond immediate cost savings. How will changes affect employee morale, institutional memory, customer loyalty, and innovation pipelines? What skills become more valuable rather than obsolete as AI handles routine tasks? Companies must invest in workforce transition, not just workforce reduction. Reskilling programs, career pathway development, and transparent communication demonstrate ethical commitment to affected employees. Organizations treating people as disposable resources suffer lasting reputational damage.
The test for 2026 is whether leaders distinguish genuine transformation from destructive cost-cutting. Lasting organizational change enhances human capabilities through technology rather than simply eliminating human involvement. Effective approaches keep experienced professionals focused on high-value activities while automating mundane tasks.
What society do we want, and what role should fully AI-driven companies play in society? Ethics also requires leaders to take a stance on these societal issues.
Business ethics demands asking difficult questions before deploying AI broadly. Will this change improve stakeholder value holistically or just shareholder returns temporarily? Does our implementation plan respect human dignity and acknowledge social responsibilities? Organizations must also consider broader societal implications of workforce displacement. Mass unemployment destabilizes communities, reduces consumer spending power, and creates political backlash against corporations. Ethical leaders recognize their decisions affect entire ecosystems beyond quarterly earnings.
Ksapa helps organizations develop responsible AI governance frameworks that balance efficiency with human-centered values. Our strategic advisory services enable leaders to assess technology implementations holistically, identifying opportunities and risks. We design transition programs supporting affected workforces while positioning companies for sustainable competitive advantage.
Ethics as Anchor Amid Geopolitical Chaos and Market Uncertainty
Corporate Assets and Value Chains Under Radical Stress Test
Geopolitical fragmentation accelerates in 2026, disrupting international business operations and strategic planning assumptions.
- International trade agreements are under political attack, and supply chains are fragmenting along new ideological lines. Wars continue to reshape regional dynamics and access to resources and supplies, forcing a redesign of value chains.
- Pandemic risks persist, alongside emerging threats to health associated, for example, with the widespread presence of microplastics in food chains. Climate and environmental disruptions (such as water stress) are exacerbating the vulnerabilities affecting the ecosystems that support the proper functioning of value chains.
- Political instability is spreading in both democratic and authoritarian systems, creating unpredictable regulatory environments. Currency fluctuations, inflationary pressures, and debt crises are complicating operational challenges, making it difficult to determine the direction of investment decisions that will ensure the adaptation of operations and value chains to this difficult-to-grasp context.
This uncertainty paralyzes decision-making for organizations accustomed to relative stability and predictable trajectories. Traditional strategic planning horizons compress as executives struggle to forecast even near-term conditions. Risk management frameworks designed for normal volatility prove inadequate for current turbulence.
Trust remains the only solid asset today that enables companies to navigate uncertainty and retain the support of stakeholders who are essential to their success.
Yet business remains fundamentally transactional, depending on trust between parties engaging in exchange.
- Investors commit capital based on confidence in leadership integrity and strategic coherence.
- Consumers purchase products reflecting values they admire or aspire toward.
- Employees dedicate careers to organizations whose missions resonate with personal purpose and ethical standards.
- Suppliers invest in relationships with partners demonstrating reliability and fair dealing.
- Communities support businesses contributing positively to local well-being.
In uncertain times, clear ethical foundations become competitive differentiators rather than compliance burdens. Companies anchored in consistent values navigate volatility more successfully because stakeholders trust their commitments. Brand strength derives from authentic alignment between stated principles and operational reality. Leadership matters profoundly when external circumstances create confusion and anxiety. Executives embodying ethical clarity inspire confidence even when specific outcomes remain uncertain. People want to believe in leaders who prioritize long-term stakeholder value over short-term opportunism.
The transactional nature of business depends on reputation, which reflects accumulated evidence of ethical behavior. Organizations that compromise principles under pressure lose credibility difficult to rebuild. Stakeholders remember who maintained integrity when circumstances incentivized expedient choices. Geopolitical chaos tempts businesses toward protective measures that may violate ethical standards. Exploiting regulatory gaps, shifting risks to vulnerable partners, or abandoning commitments to affected communities. These actions generate immediate relief but corrode foundational trust supporting long-term success.
Maintaining Core Values Regardless of External Turbulences is More Critical Than Ever to Nurture Trust With Stakeholders
Admittedly, investors can exert pressure to encourage actions that boost short-term returns. All of this is true. But stakeholders are increasingly distinguishing between organizations pursuing short-term strategies and those building sustainable value. This does not target the same shareholders, the same employees, and ultimately the same customers. This leaves companies that need to stay in close contact with these long-term stakeholders. For them, being ethically grounded means maintaining fundamental values regardless of external turbulence. Ethical anchoring means maintaining core values regardless of external turbulence. Illustrative examples can look like:
- Honoring commitments to employees even when market conditions permit reneging.
- Treating suppliers fairly despite leverage to demand concessions.
- Investing in community resilience rather than extracting final value before exiting.
This approach requires courage because markets often reward short-term opportunism over principled consistency. Competitors may gain temporary advantage through ethical compromises. But stakeholders increasingly differentiate between organizations pursuing extractive strategies versus those building lasting value:
- Employees leave companies lacking ethical clarity for competitors offering purpose and integrity.
- Consumers boycott brands whose actions contradict stated values.
- Investors with long-term perspectives favor businesses demonstrating resilience through principled decision-making.
- Regulators scrutinize organizations whose behavior suggests prioritizing profits over responsibilities.
- Communities mobilize against corporations perceived as exploitative or indifferent to local impacts.
Ethics: a Compass Providing Decision-Making Framework When Conventional Analysis Offers No Clear Answers
The role of ethics in 2026 is providing decision-making framework when conventional analysis offers no clear answers. When geopolitical risks make every option imperfect, ethical principles help leaders choose least harmful paths. When uncertainty prevents optimizing outcomes, values ensure actions align with organizational identity. Companies must articulate core ethics clearly enough to guide choices amid ambiguity. What non-negotiable principles constrain decisions regardless of circumstances? How do stated values translate into operational policies and individual behaviors?
Ethical anchoring also requires transparency about trade-offs and limitations. Leaders cannot promise certainty but can demonstrate consistent reasoning processes based on explicit principles. Stakeholders accept difficult decisions more readily when they understand underlying values guiding them. Organizations succeeding in turbulent times will be those whose ethical foundations enable rapid adaptation without compromising identity. Flexibility in tactics combined with consistency in values creates resilient cultures navigating uncertainty. People align around shared principles even when strategies must evolve constantly.
Ksapa specializes in helping organizations embed ethics into strategic decision-making and operational systems. Our services include values clarification workshops, ethical risk assessments, stress test analysis, and stakeholder engagement processes. We support leaders developing governance frameworks that maintain principle-based consistency while enabling adaptive responses to changing conditions.
Conclusion: Ethics as Strategic Imperative for 2026 and Beyond
Business ethics in 2026 transcends compliance requirements to become strategic imperative for organizational resilience. Companies navigating AI transformation, geopolitical uncertainty, and environmental crises need ethical clarity guiding decisions. Values provide anchors when conventional analysis offers no clear answers. The year ahead tests whether leaders distinguish genuine transformation from destructive short-termism. Organizations downsizing without understanding full implications risk hollowing out competitive advantages. Those implementing AI responsibly enhance human capabilities rather than simply eliminating human involvement.
- Geopolitical chaos elevates importance of trust-based stakeholder relationships built through consistent ethical behavior.
- Brands maintaining principle-based consistency during turbulent times strengthen connections with investors, customers, employees, and communities.
- Reputation becomes competitive differentiator when external circumstances create universal anxiety.
- Environmental imperatives demand investment decisions reflecting responsibilities to future generations and broader ecosystems. Business case alone proves insufficient for transformation urgency required. Ethics provides compass for choices that build pride among stakeholders judging legacy being created.
The organizations succeeding long-term will be those integrating ethics into core strategy and operations. Not as separate function but as fundamental dimension of every decision. Not as constraint limiting actions but as framework enabling confident choices amid complexity.
Ksapa partners with forward-thinking organizations developing ethical foundations for sustainable competitive advantage. Our integrated approach combines strategic advisory, impact investment expertise, and advocacy capabilities. We help leaders navigate complexity with confidence, making decisions that honor commitments to all stakeholders while building resilient, future-ready businesses. Contact us to explore how ethical clarity can strengthen your organization’s strategic positioning for 2026 and beyond.
Président et Cofondateur. Auteur de différents ouvrages sur les questions de RSE et développement durable. Expert international reconnu, Farid Baddache travaille à l’intégration des questions de droits de l’Homme et de climat comme leviers de résilience et de compétitivité des entreprises. Restez connectés avec Farid Baddache sur Twitter @Fbaddache.